The rapidly growing global e-mobility industry requires new, innovative flame retardants and demand keeps increasing massively
Compared to classic cars with combustion engines,
more
ECHA Suggestion of classification, labelling and also restriction of selected chlorinated flame retardants paves the way for an increased need for halogen free flame retardants
The European Chemicals Agency ECHA recently propos
more
The Working Group „Flame Retardants“ brings together many participants from the flame retardants value chain and celebrates Prof. Manfred Döring’s well-deserved retirement
Finally, the meeting of the working group “F
more
“ECOFRAM" addresses the need for more sustainable flame retardants and showcases developments from science and industry
The International Conference on Eco-Friendly Flame
more
RoHS: Impact study finds positive results, review process has started
The importance of RoHS, the restriction of hazardo
more
“Fire Resistance in Plastics" addresses the need for flame retardants for e-mobility – halogen-free solutions in clear focus
The Fire Resistance in Plastics is one of the most
more
Inorganic
Mode of action: Depending on the flame retardant, cooling of the polymer, dilution of the substrate and of the combustion gases (ATH, MDH), or formation of a charred layer (Zn borate, exp.C, Nanocomposites), as well as synergism (ATO, AlOOH) may take pla
The most important flame retardants, which are also used as fillers, are aluminum trihydrate (ATH) and magnesium hydroxide (MDH). In addition, antimony trioxide (ATO) is used in large quantities as a synergist with halogenated flame retardants and PVC. Aluminum oxide hydrate (AlOOH or Boehmite) also acts as a synergist in conjunction with metal phosphinates.
Metal hydroxides
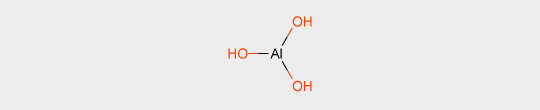
Aluminum hydroxide or aluminum trihydrate (ATH) already decomposes at around 200 °C.
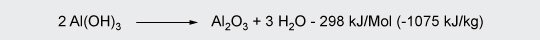
Therefore, it only can be used with plastics processed at lower temperatures such as PVC, polyethylene, ethylene/vinyl acetate-copolymers and thermosets.
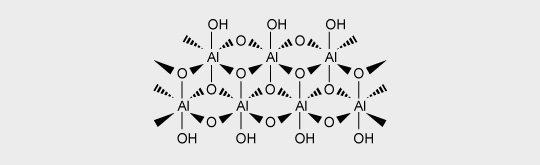
Aluminum oxide hydrate (AlooH) or Boehmite decomposes at 320 °C. It can therefore be used in engineering thermoplastics and is synergistic with metal phosphinates. It iss also used in printed circuit boards.
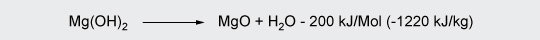
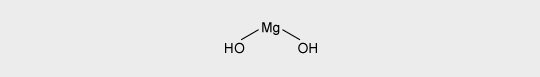
Magnesium hydroxide (MDH) decomposes at around 300 °C.
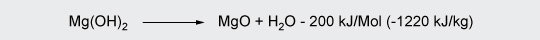
Its main applications are polypropylene, polyamides and wire & cable.
Zinc compounds
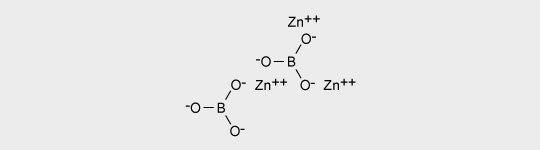
Zinc borate may partly substitute antimony trioxide in thermoplastics, inhibits afterglow and acts as a smoke suppressant. 4ZnO . B2O3 .H2O, which decomposes at 415 °C, is suitable for engineering plastics.
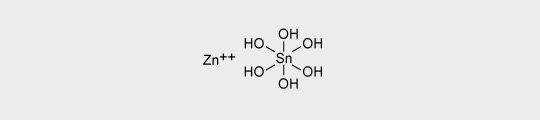
Zinc hydroxystannate is used as a smoke suppressant for PVC, unsaturated polyesters and elastomers.